Shiitake mushroom
Lentinus edodes
Black forest mushroom, 香菇 (xiāng gū, Mandarin), શિતાકેમશરૂમ (Śitākē maśarūma, Gujarati), likaha shiitake (Somali), Uyoga wa Shiitake (Swahili)
The shiitake mushroom is native to East Asia, and they have been cultivated for food and medicine for almost one thousand years. The flavorful mushroom is included in a variety of different cuisines throughout Asia in stir fries, soups, rice dishes, and more. Shiitake mushrooms did not receive significant attention in the United States until the mid-twentieth century, but today they are the most popular gourmet mushroom in North America where they are used as a more flavorful and nutritious alternative to white mushrooms. In Florida, an increasing number of home gardeners are growing shiitake mushrooms on hardwood logs and wood-shavings.
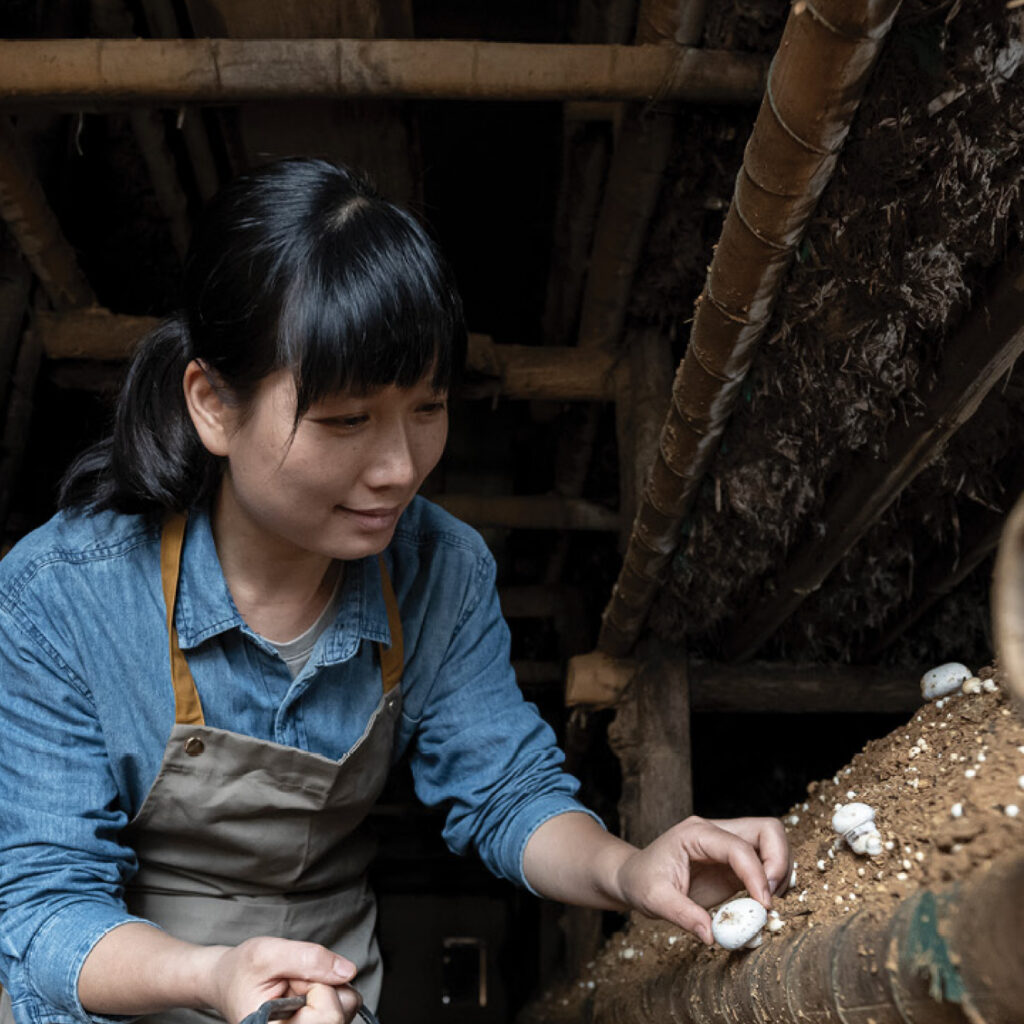

The shiitake mushroom originated in warm and moist climates in East Asia, and they were first cultivated in China by Wu San Kwung in the Song Dynasty in 1209 CE. The oldest book on shiitake cultivation dates to 1796 in Japan by Satō Chūryō. The ancient Japanese technique inoculates Shii tree logs with mushroom spores by placing them in areas where the mushrooms were already growing. The Shii tree is where the shiitake gets its name. Cultivation in the United States did not begin until nearly 200 years later in 1972 when a ban on the importation of fungal spores was lifted, and a 1982 industry report on opportunities in the shiitake industry launched commercial production in North America. Today shiitake mushrooms account for a quarter of global commercial mushroom production, and an increasing number of Americans are growing shiitake mushrooms at home on hardwood logs and wood-shavings.
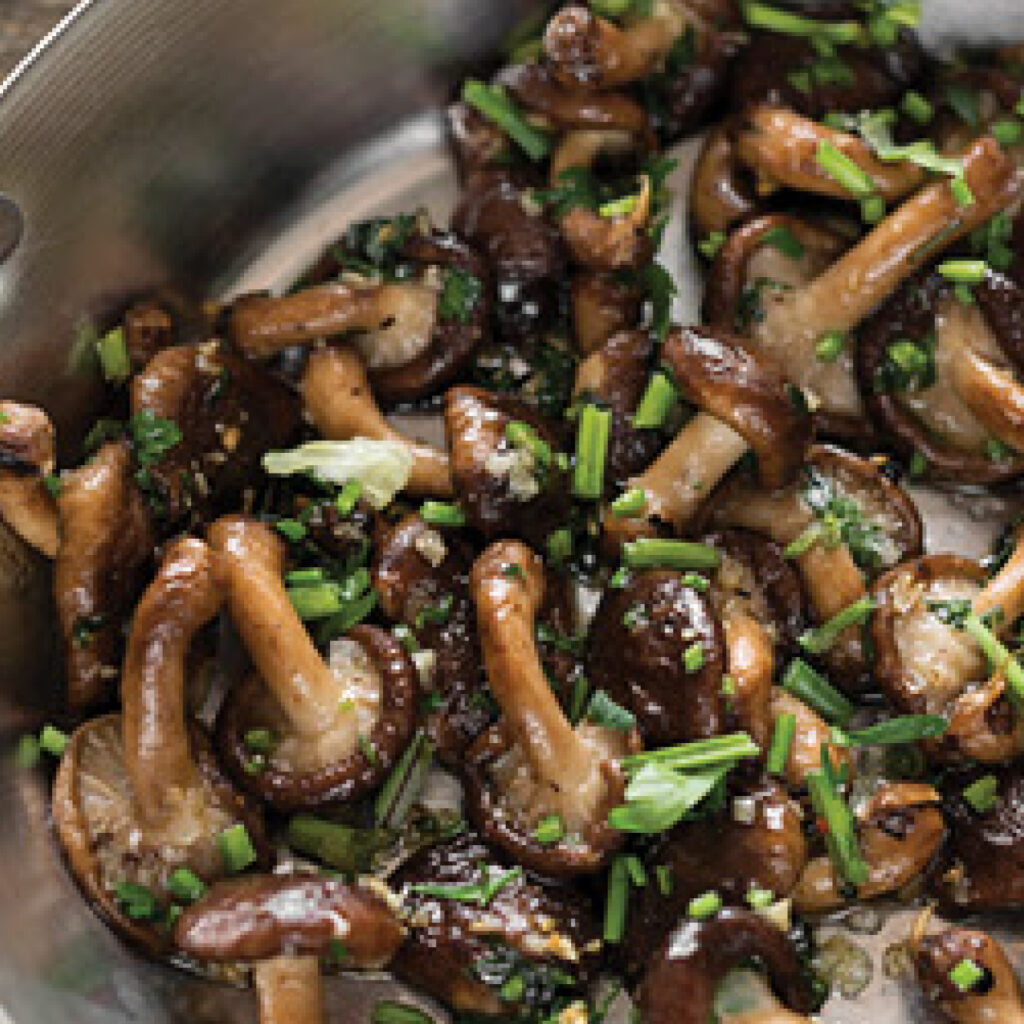
Fresh and dried shiitake mushrooms have been used as food and medicine for over 1,000 years. They can be consumed raw or cooked, and they dehydrate well for long-term storage. In Japanese cuisine shiitake are added to miso soup, simmered in ramen bowls called nimono and to mushroom-rice dishes called takikomi gohan. Chinese recipes use them in stir-fries, lo mein, steamed buns called baozi, and braised mushrooms with bok choy called xiang gu cai xin. Similarly, Korean cuisine includes a stir-fried shiitake mushroom dish called yogo-bokkeum. In the United States, shiitake mushrooms are often used as a more flavorful and nutritious alternative to white mushrooms and to make Asian-inspired or fusion recipes.

Shiitake mushrooms are rich in vitamins C, A, B12, D, B2; iron, calcium, copper, selenium, zinc, and manganese.


Inoculate logs or substrate September through December; incubation may take up to 18 months . Harvest May through July.
To plan a heritage garden, download the ‘Planning a Florida Heritage Garden (PDF).’

Santa Fe College Partnered with Multiple Organizations in a Collaborative Effort to Bring Awareness of the Heritage Plants In Florida.
BY CULTURAL HISTORY
BY GROWING SEASON
DROUGHT TOLERANT PLANTS
Commitment to Equal Access and Equal Opportunity
Santa Fe College is committed to an environment that embraces diversity, respects the rights of all individuals, is open and accessible, and is free of harassment and discrimination. For more information, visit sfcollege.edu/eaeo or contact equity.officer@sfcollege.edu.
SACSCOC Accreditation Statement
Santa Fe College is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC). For more information, visit sfcollege.edu/sacscoc.
