Ginger
Zingiber sp
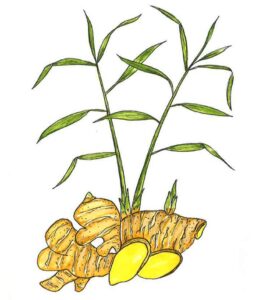




Ginger is propagated from pieces of the root. Dry three-inch pieces for a few days before planting at least three inches deep and one foot apart in well-drained soil after the possibility of frost but before the summer heat sets in (April-June). Ginger likes shade and will do well in partial and even full shade. Be attentive to keeping the soil moist for 2-3 weeks, at which time the young sprouts come up through the soil. Shade dry harvested roots until the skin becomes dry before using. (It is important to note that ginger root in the grocery store may have been irradiated to prevent sprouting and will not grow in the garden.) To plan a heritage garden, download the ‘Planning a Florida Heritage Garden (PDF).’

Santa Fe College Partnered with Multiple Organizations in a Collaborative Effort to Bring Awareness of the Heritage Plants In Florida.
BY CULTURAL HISTORY
BY GROWING SEASON
DROUGHT TOLERANT PLANTS
Commitment to Equal Access and Equal Opportunity
Santa Fe College is committed to an environment that embraces diversity, respects the rights of all individuals, is open and accessible, and is free of harassment and discrimination. For more information, visit sfcollege.edu/eaeo or contact equity.officer@sfcollege.edu.
SACSCOC Accreditation Statement
Santa Fe College is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC). For more information, visit sfcollege.edu/sacscoc.
